


Endometriosis is a chronic medical condition where tissue similar to the lining inside the uterus, known as the endometrium, starts growing outside the uterus. This abnormal tissue can be found on the ovaries, fallopian tubes, the outer surface of the uterus, and other organs within the pelvis. Endometriosis can cause significant pain, fertility issues, and a range of other symptoms that can severely impact a person's quality of life. This article provides an overview of endometriosis, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
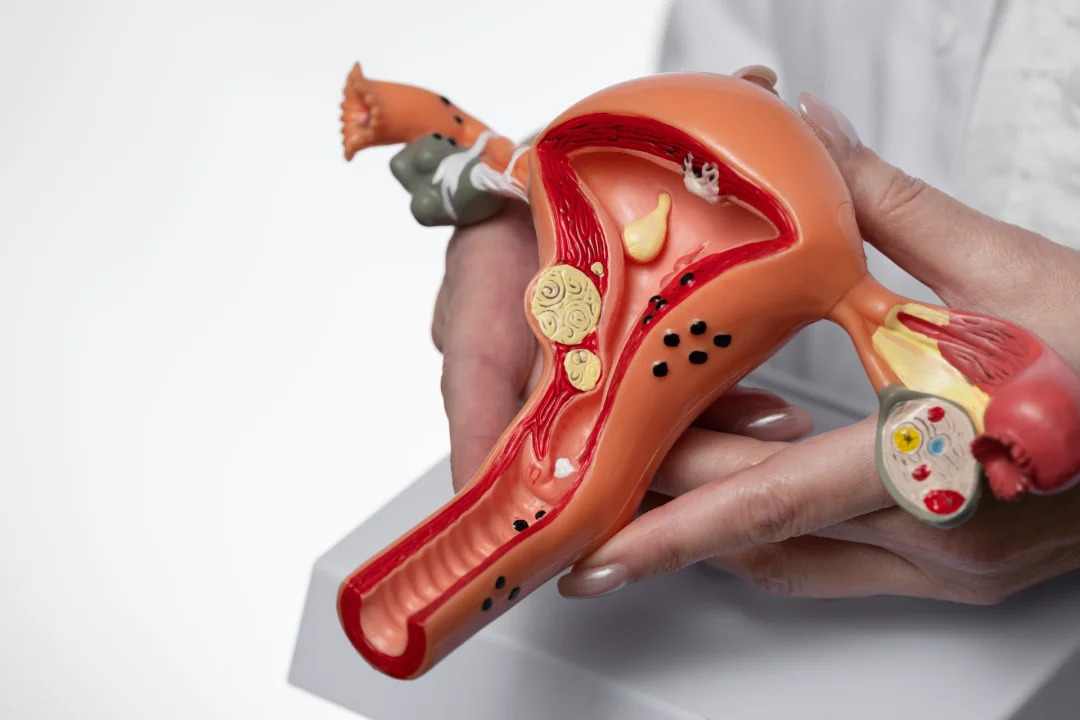
In endometriosis, endometrial-like tissue grows in areas where it does not belong. During the menstrual cycle, this tissue responds to hormonal changes by thickening, breaking down, and bleeding. However, unlike the tissue in the uterus, which leaves the body during menstruation, this displaced tissue has no way to exit. The trapped blood and tissue can lead to inflammation, scar tissue formation, and adhesions, which can cause organs in the pelvic region to stick together.
The exact cause of endometriosis is not well understood, but several theories exist:
Menstrual blood flows backward through the fallopian tubes into the pelvic cavity instead of leaving the body, allowing endometrial cells to implant and grow outside the uterus.
Hormones such as estrogen may transform embryonic cells into endometrial-like cell implants during puberty.
After surgeries like a hysterectomy or C-section, endometrial cells may attach to the surgical incision.
Problems with the immune system may make the body unable to recognize and destroy endometrial-like tissue outside the uterus.
The severity of symptoms can vary widely among individuals and does not always correlate with the extent of the disease. Common symptoms include:
Often associated with menstrual periods, pain can occur before and during menstruation, and can be severe. It may also be chronic (lasting six months or more).
Heavy periods (menorrhagia), bleeding between periods, or periods that last longer than normal.
Pain during or after sex is common with endometriosis.
These symptoms are most likely during menstrual periods.
Endometriosis is sometimes first diagnosed in those seeking treatment for infertility.
Fatigue, diarrhea, constipation, bloating, and nausea, especially during menstrual periods.
Diagnosing endometriosis can be challenging, as symptoms often overlap with other conditions. A combination of the following methods is typically used:
A thorough medical history and pelvic examination.
Ultrasound or MRI may be used to identify large endometrial cysts or to evaluate the pelvis.
The gold standard for diagnosis, this minimally invasive surgical procedure allows direct visualization and biopsy of endometrial tissue.
Treatment for endometriosis depends on the severity of symptoms, the extent of the disease, and whether the person wishes to become pregnant. Options include:
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen can help relieve pain.
Birth control pills, hormonal IUDs, GnRH agonists, and other hormone-based treatments can reduce or eliminate menstruation and relieve pain.
Used both for diagnosis and treatment, it involves the removal or destruction of endometrial growths.
A more invasive surgery for severe cases, involving a larger incision in the abdomen.
Removal of the uterus, and sometimes the ovaries, may be considered in severe cases when other treatments have failed.
Options like in vitro fertilization (IVF) may be recommended for those with endometriosis-related infertility.
Endometriosis is a complex condition that can significantly impact a person's physical and emotional well-being. Early diagnosis and a personalized treatment plan are crucial in managing symptoms and improving quality of life. Individuals experiencing symptoms of endometriosis should consult with the most experienced gynecologist, Dr. Sukriti Sharma, in Jalandhar.